一、肺癌筛查带来的益处
- 降低肺癌死亡率:筛查发现的肺癌多数是早期,减少了肺癌的死亡率,减少治疗相关死亡率;
- 只要恰当选择人群,总体的费效比很高;
- 降低相关疾病(COPD等)负荷;
- 降低治疗负荷(早期患者可接受的治疗方式较晚期更优);
- 促进健康的生活方式(戒烟);
- 降低焦虑/心理负担。
二、肺癌筛查带来的风险
- 检出侵袭性小肿瘤或惰性疾病并无意义;
- 对于进展快的小结节可能并不影响结局;
- 因假阳性检测结果,导致更多的不必要的检查和心理上的焦虑;
- 诊断引起的并发症和偶发的创伤
- 假阳性结果
- 假阴性结果
- 不必要的检测和流程
- 暴露于放射线辐射,增加患癌风险
- 检测成本
三、有关的数据
- 首次肺癌筛查的人群中有约24%发现肺结节,但其中仅约4%为肺癌。
- NLST研究中,39%筛查者至少有一次假阳性结果
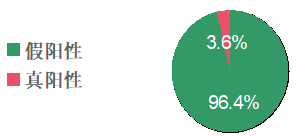
图1. 肺癌筛查假阳性率高
每1000人可减少3例肺癌死亡,但同时也会导致365例假阳性,有18例接受有创检查,少于1例会出现检查导致的重大并发症。
参考文献 - NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Lung Cancer Screening. 2021. Version 1. LCS-1+LCS-2
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 2021. Version 5. PREV‐1
- ACCP. Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer,3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. 2013
- 中国临床肿瘤学会指南工作委员会.中国临床肿瘤学会 (CSCO) 非小细胞肺癌诊疗指南. 2020.
- ACCP. Evaluation of Individuals With Pulmonary Nodules: When Is It Lung Cancer?Evaluation of Individuals With Pulmonary Nodules: Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2013;143(5_suppl):e93S-e120S. doi:10.1378/chest.12-2351
- Veronesi G,Bellomi M,Mulshine JL,et a1.Lung cancer screening with low-dose computed tomography:a non-invasive diagnostic protocol for baseline lung nodules[J].Lung Cancer,2008,61(3):340-349.doi:10.1016/j.1ungcan.2008.01.001.
- ACCP. Screening for Lung Cancer. Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer,3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. 2013
- Infante M, Berghmans T, Heuvelmans MA, Hillerdal G, Oudkerk M. Slow-growing lung cancer as an emerging entity: from screening to clinical management.Eur Respir J. 2013 Dec;42(6):1706-22. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00186212. Epub 2013 May 16.
|